Introduction and benchmarking of pyMLST: open-source software for assessing bacterial clonality using core genome MLST
ABSTRACT
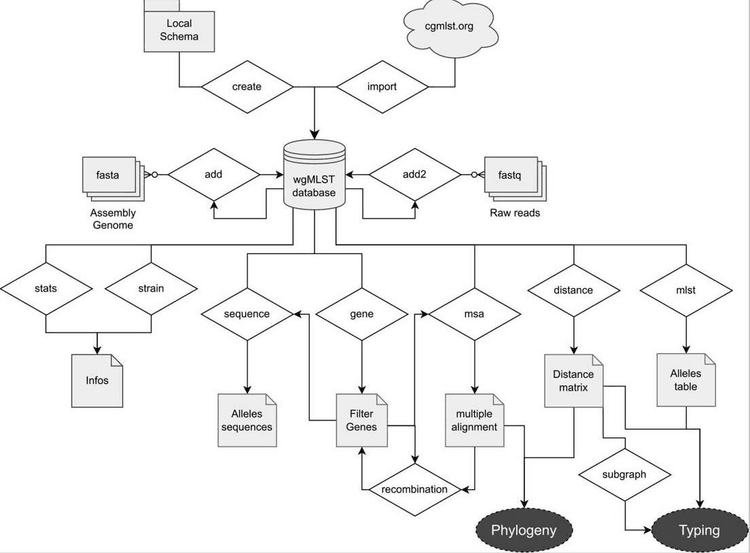
Core genome multilocus sequence typing (cgMLST) has gained in popularity for bacterial typing since whole-genome sequencing (WGS) has become affordable. We introduce here pyMLST, a new complete, stand-alone, free and open source pipeline for cgMLST analysis. pyMLST can create or import a core genome database. For each gene, the first allele is aligned against the bacterial genome of interest using BLAT. Incomplete genes are aligned using MAFT. All data are stored in a SQLite database. pyMLST accepts assembly genomes or raw data (with the option pyMLST-KMA) as input. To evaluate our new tool, we selected three genome collections of major bacterial pathogens (Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus) and compared them with pyMLST, pyMLST-KMA, ChewBBACA, SeqSphere and the variant calling approach. We compared the sensitivity, precision and false-positive rate for each method with those of the variant calling approach. Minimal spanning trees were generated with each type of software to evaluate their interest in the context of a bacterial outbreak. We found that pyMLST-KMA is a convenient screening method to avoid assembling large bacterial collections. Our data showed that pyMLST (free, open source, available in Galaxy and pipeline ready) performed similarly to the commercial SeqSphere and performed better than ChewBBACA and pyMLST-KMA.